Lamps without reflector which are - in general - used for home lighting:
- GL = Incandescent lamps
- HAL = Halogen lamps
- ESL = Energy saving lamps (compact fluorescent lamps with standard base)
- LED = LED lamps (for direct exchange with incandescent lamps)
Regulations
For the lamp types mentioned above requirements of efficiency and functionality will be set according to a certain time scheme. Lamps which do not meet those requirements must not carry the CE marking any more and must not be brought to market by the manufacturer.
Any lamp produced previously which has got a CE marking even though it may not literally be entitled to do so, may still be sold off the warehouse stock of retail.
Certain technical data such as, for example, number of switchings until failure or mercury content must be shown on packaging in a defined way and must be shown as free access information e.g. in the internet. There, many more (technical) details have to be published.
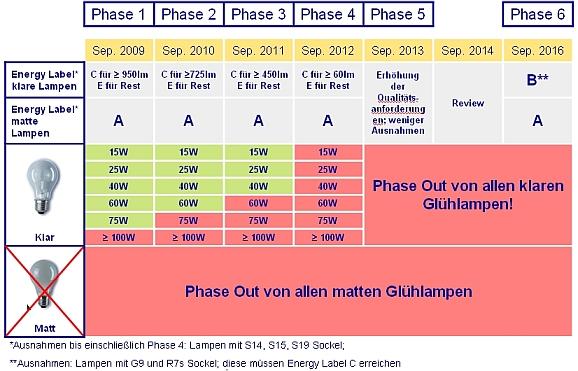
Timetable of measures
2009 Only lamps with energy label A may be called energy saving lamps.
frosted GL must be replaced by lamps with energy label A
clear GL from about 100W (950 lm) min. energy label C, others energy label E
functional quality requirements for ESL with energy label A
(e.g. MSL= B50 min. 6000h, Ra ≥ 80, at 200h less than 2% early failures)
2010 clear GL from about 75W min. (725 lm) energy label C, others energy label E
2011 clear GL from about 60W min. (450 lm) energy label C, others energy label E
2012 clear GL from about 10W (60 lm) min. energy label C
2013 GL with base S14, S15 and S19 and low voltage lamps min. energy label C
More demanding functional quality requirements for ESL with energy label A
(e.g. B70 min. 6000h, at 400h less than 2% early failures)
2018 GL from 60 lm min. energy label B, lamps with G9 or R7s-base still min. energy label C
(Step 6 has been postponed to 2018 from originally 2016).